Resistor / Resistance: It is the property of a material which opposes the flow of electric current through it. Conductors have low resistance while insulators have very high resistance. It is measured in Ohms.
Search This Blog
SV0435 Z INV. LOW VOLT DC LINK
SV0444 X1 INV. COOLING FAN FAILURE ALARM
This type of alarm occurs when the servo drive cooling fan has gone bad.
Remedy:
1. Check alarm no 1 on the servo drive
2. Replace faulty drive other remove and re-insert servo drive cooling fan
9031 SPN 1 MOTOR LOCK OR V-SIG LOS ALARM
PLC brand and Software name
| S.No. | PLC’s Brand | Developed Country | Software |
| 01 | AB PLC | United State | RS Logix (RS Logix 5, RS Logix 500 and RS Logix 5000) |
| 02 | Siemens PLC | Germany | Step 5- Micro wins Step 7- Simatic Manager |
| 03 | ABB PLC | Switzerland | Automation Builder AC010 AC500 |
| 04 | Delta PLC | Taiwan | WPL Soft ISP Soft |
| 05 | Schneider PLC | Europe | PL7 TwidoSuite ProWORX 32 |
| 06 | Mitsubishi PLC | Japan | Gx Developer Gx Works 2 MELSOFT series |
| 07 | Omron PLC | Japan | CX-One CX programmer |
| 08 | Hitachi PLC | Japan | EH-150 |
| 09 | General Electric PLC | United State | Durus |
| 10 | Honeywell PLC | United State | HRA |
| 11 | FATEK PLC | Taiwan | WinProladder |
| 12 | Bosch | Germany | Bosch Rexroth |
What is TIA Protal ?
Totally Integrated Automation Portal (TIA Portal). It gives you unrestricted access to the complete range of digitalized automation services, from digital planning to integrated engineering and transparent operation. With TIA Portal you gain valuable competitive advantages.
The Totally Integrated Automation Portal (TIA Portal), provides an engineering framework for implementing automation solutions in all industries around the globe. From designing, commissioning, operating, and maintaining to upgrading automation systems, the TIA Portal saves engineers time, cost, and effort. SIMATIC STEP 7 in the TIA Portal is the software for the configuration, programming, testing, and diagnosis of all modular and PC-based SIMATIC controllers, and includes a variety of user-friendly functions.
Software in TIA Portal
With TIA Portal you not only integrate the basic software (STEP 7, WinCC, SINAMICS Startdrive, SIMOCODE ES and SIMOTION SCOUT TIA), but you also benefit from additional functionalities provided by new options such as TIA Portal Multiuser Engineering and Power Management with SIMATIC Energy Suite via a single interface. That’s why TIA Portal offers everything you need for end-to-end engineering, both now and in the future.
Siemense 840D PLC General Reset Procedure
The following steps with the PLC start-up switch S4 will cause a PLC GENERAL RESET:
1. Turn to position “2” (STOP operating state)
PS LED lights up.
2. Turn to position “3” (MRES operating state, request general reset) and hold
in this position (for approx. 3 second) until the PS STOP LED lights up again.
PS LED goes out and comes on again.
3. Within 3 second, turn to the
STOP-MRES-STOP (“2”–“3”–“2”) positions
PS LED PS first flashes at approx. 2 Hz and then lights up again
PF LED lights up
4. Once the PS and PF LEDs are lit, turn the switch S4 to position “0”
The PS and PF LEDs goes out and the PR LED (green) lights up
A general reset of the PLC is complete. It is now in cyclical mode.
CNC Machine Spindle
Resistance, Inductor,Capacitor
1.Resistor / Resistance: It is the property of a material which opposes the flow of electric current through it. Conductors have low resistance while insulators have very high resistance. It is measured in Ohms
2.Inductor / Inductance: It is the property of a coil to resist any change in electric current flowing through it. Self inductance is caused when a coil resists the current change through itself. Mutual inductance occurs when a secondary coil opposes current change in a primary coil. Inductance is measured in Henry.
3.Capacitor / Capacitance: The amount of charge that can be stored inside a capacitor at a given voltage is called Capacitance. It gets charged when charges are forced into the positive (or upper) plate of the capacitor due to emf. Similarly, it discharged when charges are forcefully pulled out of the capacitor. Capacitance is measured in Farad.
AC and DC
Power Transformer

Grinding Machine
Following are the types of grinding machines:
1.Bench Grinder: These types of grinding machines are fixed on a workbench or table. Gear or pulley is fitted in it. For rotating the big-size gears or pulley a handle is also fixed. It contains one or two grinding wheels. Edges of cutting tools can be made with this grinder. Provision can be made to operate these with power also.
2.Hand Grinder: This grinder is also fixed on the workbench or table. There is a provision of moving the grinding wheels with a level.
3.Pedestal Grinder: These types of grinding machines are operated with electric power. This is fitted on a pedestal frame separately on the ground. A grinder wheel is fitted each on both sides of the shaft of the electric motor.Tools rests are also provided with them. These are the most widely used in the workshops
4.Portable Grinder: This is a small grinder operated with electric power. It can be easily carried anywhere. Grinding can be done by holding it in hand. It is used for cleaning heavy welding jobs.
5.Flexible Grinder: Flexible shaft is fitted on the motor shaft with the help of a coupling. On one end of the shaft, a grinding wheel and handle are provided. Large jobs can be easily grinded with this grinder.
6.Precision Grinder: In this type of grinder, a movable spindle is fitted in the grinding wheel. This spindle is fitted on a table along with its motor. With this spindle, the grinding wheel can be turned in forward, backward, left, or right direction in running condition. Jobs of excellent finish and accuracy are grinded with it.
7.Surface Grinder: A surface grinder is a reciprocating grinding machine used for making flat surfaces on workpieces. It can form surfaces with greater precision.
8.Swing Frame Grinder: This grinder consists of a 2 or 3-meter long frame with a grinding wheel that is suspended at its center of gravity so that it can move freely.
Classification of Grinding Machine
Basically Grinding machine can be classified into two categories which are:
1.Non-Precision Grinding Machine: By this grinding machine, such materials are removed from workpieces that are rough such as materials made from casting, forging, etc.
Non Precision Grinders are :
1.Bench Grinder
2.Pedestal Grinder
3.Portable Grinder
4.Flexible Shaft Grinder
5.Swing Frame Grinder
2.Precision Grinding Machine: By this grinding machine, such materials are removed from workpieces that are soft and required precise surface finished.
Precision Grinders are:
Surface Grinder
1.Horizontal Spindle Reciprocating Table Horizontal Spindle Rotary Table
2.Vertical Spindle Reciprocating Table
3.Vertical Spindle Rotary Table
Cylindrical Grinder
1.External Cylindrical Grinder
2.Internal Cylindrical Grinder
3.Universal Cylindrical Grinder
4.Centerless Grinder
A.Tool and Cutter Grinder
B.Special Purpose Grinding Machine
Other Grinding Machine: It may be precision or non precision grinding machine.
1.Wet Grinding : In most of the grinding machines, there is a provision of a regular flow of coolant apparently on the workpiece where the wheel touches.
2.Dry Grinding : There is no arrangement of coolant system with the grinding machine and the workpiece is finished on that grinding machine then it is called dry grinding.
Grinding Defects
There are the following grinding defects found during the grinding operation.
1.Overheated Spots
2.Chatter Marks
3.Rapid wear of the Wheel
Causes of Overheated Spots
The excess wheel speed and feed.
Wheel in glazing condition.
Not using enough coolant.
Remedies of Overheated Spots
Use the right speed and feed.
Dress the wheel.
Use sufficient coolant
Causes of Chatter Marks
Wheel not mounted properly.
Slackness in the spindle.
Wheel unbalanced.
Not clamping properly job.
Excess cut depth for the machine.
Remedies of Chatter Marks
Mount the wheel correctly.
Remove slackness of spindle.
Balance the wheel.
Clamp the job properly.
Use the correct cut depth.
Causes of Rapid Wear of the Wheel
Wheel too soft.
Grinding wheel speed is less than the permissible speed.
Remedies Rapid Wear of the Wheel
Use the correct grade of the wheel.
Increase the wheel speed to the approved speed.
Adjustable Spanner
Adjustable spanner is an open-ended wrench with a moveable jaw. Its function is the same as any regular spanner to grip fasteners, such as nuts and bolts.
Clamp and Types of Clamp
Production and Types of Production
What is production?
Production is a process of value addition, which is developed to transform a set of input elements like man, raw material, capital, energy, information into finished products and services in proper quality and quantity.
“Production is the organised activity of transforming resources into finished products in the form of goods and services; the objective of production is to satisfy the demand for such transformed resources”
Punch and Types of Punch Tool
Types of punches are as follows:
1. Centre punch
2.Prick punch
3.Solid punch
4.Transfer punch
5.Drive punch
6.Pin punch
7.Roll pin punch
8.Hollow punch
9.Dot punch
10.Letter stamps
11.Tablet punch
1024 PMM Axis Not Ready
9030 SPN 1 Overcurrent Pow Circuit Alarm
This type of alarm comes when there is a load on the spindle or one of the servo axis due to current increases and the driver goes to tripped
Plier and Types of Pliers
MTBF ( Mean Time Between Failures )
What is mean time between failures?
MTBF (mean time between failures) is the average time between repairable failures of a technology product. The metric is used to track both the availability and reliability of a product. The higher the time between failure, the more reliable the system.
MTBF calculation Formula:
MTBF Example :
Over a period of time the following information is available:
Total Production Time (PT): 1,240 minutes
Total Downtime (DT): 1.5 hours (watch the unit of measures)
Number of Failures (F): 25
Determine the MTBF:
The first step is to determine the Uptime (UT) which = PT - DT
Uptime (UT) = 1,240 minutes - 90 minutes = 1,150 minutes
MTBF = UT / F = 1,150 / 25 = 46 minutes
MTTR ( Mean Time To Repair )
What is MTTR?
Mean time to repair (MTTR) is a maintenance metric that measures the average time required to troubleshoot and repair failed equipment. It reflects how quickly an organization can respond to unplanned breakdowns and repair them.
MTTR calculates the period between the start of the incident and the moment the system returns to production.
Mean time to repair (MTTR): As described above, MTTR is the average time it takes for a failed system to be fixed and restored to full functionality. It is a relative measure, and therefore, depending on the system, could be measured in anything from minutes to days.
This takes into account the time to:
1.Notify technicians
2.Diagnose the issue
3.Fix the issue
4.Allow the equipment to cool down
5.Reassemble, align, and calibrate the asset
6.Set up, test, and start up the asset for production
Calculate MTTR by adding up the total time spent on repairs during any given period and then dividing that time by the number of repairs.
Mean Time To Repair = (Total downtime) / (number of failures)
MTTR Example :
Over a period of time the following information is available:
Total Production Time (PT): 1,240 minutes
Total Downtime (DT): 1.5 hours (watch the unit of measures)
Number of Failures (F): 25
Determine the MTTR:
MTTR = Total Downtime / Number of Failures = 90 minutes / 25 failures
MTTR = 3.6 minutes per failure
OEE ( Overall Equipment Effectiveness )
What is OEE?
Overall equipment effectiveness is a maintenance KPI that measures an asset’s level of productivity. OEE is a combination of three factors that tell you how efficient an asset is during the manufacturing process: asset availability, asset performance, and production quality.
1. Availability – How often does the asset function when needed?
2. Performance – How much does the asset produce?
3. Quality – How many high-quality items does the asset produce?
When an asset operates with an OEE of 100%, it means that every item it produces is without defect (quality), it is producing as fast as possible (performance), and it experiences no unplanned downtime (availability).
OEE Factors :
OEE Calcutation Formula :
OEE = Availability (A) × Performance (P) × Quality (Q)
Benchmarking OEE :
Ideal Availability 90% Normal 79%
Ideal Performance 95% Normal 80%
Ideal Quality 99.9% Normal 95%
Ideal OEE 85% Normal 60%
How is OEE used?
Overall equipment effectiveness is an indicator of how efficient the manufacturing process is. It can be used to identify underperforming assets and connect poor performance with one or more of the three main factors (availability, performance and quality). Once the source of the problem is pinpointed, the underlying issues can be investigated and improved.
Six Big Losses :
Maintenance and Types of Maintenance
What is Maintenance?
Maintenance, otherwise known as technical maintenance, refers to a set of processes and practices which aim to ensure the continuous and efficient operation of machinery, equipment, and other types of assets typically used in business. Diligence in implementing an effective maintenance program is essential to the successful performance and longevity of machinery, assets, facilities, and entire businesses.
Types of Maintenance :
There are different types of maintenance work, each designed for specific scenarios.
1. Breakdown Maintenance
2. Planned Maintenance
A. Preventive Maintenance
B. Predictive maintenance
C. Corrective Maintenance
3. Routine Maintenance
1. Breakdown Maintenance
Breakdown maintenance, sometimes called run-to-failure maintenance, occurs when an asset completely breaks down and needs repair to resume operation.
The breakdown maintenance is a type of maintenance that involves using a machine until it completely breaks down and then repairing it to working order.For example, this type of maintenance would occur if you wait until a machine stops working before fixing it.
Breakdown maintenance is triggered by either:
☆ A planned event, such as run-to-failure maintenance.
☆ An unplanned event, such as the need for reactive or corrective maintenance.
2. Planned Maintenance
Where routine maintenance may happen on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis, planned maintenance may be scheduled once per year or as needed. This is because planned maintenance is more time-consuming, expensive, and thorough—often requiring the services of a specialist. In the context of maintaining an air-conditioning unit, routine maintenance is taking out and washing the filters once per month, while planned maintenance is hiring an HVAC professional to check refrigerant levels, possible leaks, and measure airflow through the evaporator coil.
A. Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance (PM) is the regular and routine maintenance of equipment and assets in order to keep them running and prevent any costly unplanned downtime from unexpected equipment failure.Preventive maintenance is the act of performing regularly scheduled maintenance activities to help prevent unexpected failures in the future. Put simply, it's about fixing things before they break.
Preventive maintenance (PM) is a simple and popular maintenance strategy. Preventive maintenance, also known as preventative maintenance, can help extend asset life, increase productivity, and ultimately decrease maintenance spending.
B. Predictive Maintenance
This maintenance type focuses on techniques used to determine the appropriate schedule for planned and corrective maintenance. Its primary goal is to predict, through a variety of testing methods, when a machine will start experiencing severe wear and tear so corrective maintenance can be scheduled without affecting productivity goals and before the machine breaks down.
C. Corrective Maintenance
Corrective maintenance is a maintenance task performed to identify, isolate, and rectify a fault so that the failed equipment, machine, or system can be restored to an operational condition within the tolerances or limits established for in-service operations.
Corrective maintenance covers maintenance tasks that are undertaken to identify, isolate and repair a fault in order to restore equipment, a machine or a system to an operational condition so it can perform its intended function.
Corrective maintenance is often associated to breakdowns or reactive maintenance and can include troubleshooting, disassembly, adjustment, repair, replacement and realignment.
3. Routine Maintenance
This type of maintenance, also referred to as preventive maintenance, is implemented on a fixed schedule and typically includes activities such as inspecting, cleaning, washing, replacing, and checking. It is typically performed in the downtime between shifts or on weekends to avoid affecting productivity goals. Routine maintenance has two objectives; to identify existing issues so they can be corrected ASAP and to prevent possible issues from becoming a reality through consistent care.
SV0368 B axis Serial data error alarm
Cutting Tool Insert
Screw Driver
Screw driver is a tool, manual or powered, used for turning screws. A typical simple screwdriver has a handle and a shaft, ending in a tip the user puts into the screw head before turning the handle.
1825 SERVO LOOP GAIN PARAMETER
Valid data range 1 to 9999
1821 REF. COUNTER PARAMETER
Valid range 0 to 99999999
1425 REF. RETURN FL PARAMETER
Set feedrate (FL rate) after deceleration when the reference position returnis performed for each axis.
1430 MAX CUT FEEDRATE PARAMETER
Specify the maximum cutting feedrate for each axis.A feedrate for each axis is clamped in cutting feed so that it does not exceed the maximum feedrate specified for each axis
1815 SERVO AXIS REFERENCE PARAMETER
When the parameter 1815 APZ column changes to a zero, this means the absolute encoder in the respective axis has lost its zero position. When you turn it back to a 1, this enables you to move the axis back to zero if it is not.
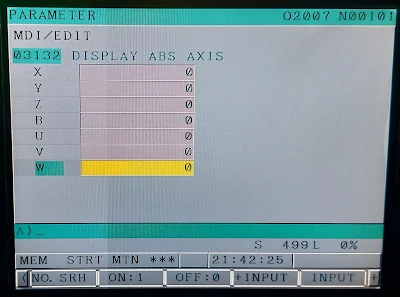
3133 Display Rel Axis Parameter
Check Parameter 3133, this is ASCII control characters for the axis letters. If set to 0's then the axis names on the screen for relative will be the same as all the others.